Command line: pline
Specify start point: Specify a point (1)
Current line-width is
Specify next point or [Arc/Close/Halfwidth/Length/Undo/Width]: Specify a point (2) or enter an option
The PLINEGEN system variable controls the linetype pattern display around and the smoothness of the vertices of a 2D polyline. Setting PLINEGEN to 1 generates new polylines in a continuous pattern around the vertices of the completed polyline. Setting PLINEGEN to 0 starts and ends the polyline with a dash at each vertex. PLINEGEN does not apply to polylines with tapered segments.
 Next Point
Next Point
Draws a line segment. The previous prompt is repeated.
Arc
Adds arc segments to the polyline.
Specify endpoint of arc or
[Angle/CEnter/CLose/Direction/Halfwidth/Line/Radius/Second pt/Undo/Width]: Specify a point (2) or enter an option
Note - For the Center option of the PLINE command, enter ce; for the Center object snap, enter cen or center.
Endpoint of Arc
Draws an arc segment. The arc segment starts at the last point tangent to the previous segment of the polyline. The previous prompt is repeated.
Angle
Specifies the included angle of the arc segment from the start point.
Specify included angle:
Entering a positive number creates counterclockwise arc segments. Entering a negative number creates clockwise arc segments.
Specify endpoint of arc or [Center/Radius]: Specify a point or enter an option
Endpoint of Arc
Specifies the endpoint and draws the arc segment.
Center
Specifies the center of the arc segment.
Specify center point of arc:
Radius
Specifies the radius of the arc segment.
Specify radius of arc: Specify a distance
Specify direction of chord for arc
Center
Specifies the center of the arc segment.
Specify center point of arc: Specify a point (2)
Specify endpoint of arc or [Angle/Length]: Specify a point (3) or enter an option
Endpoint of Arc
Specifies the endpoint and draws the arc segment.
Angle
Specifies the included angle of the arc segment from the start point.
Specify included angle:
Length
Specifies the chord length of the arc segment. If the previous segment is an arc, the new arc segment is drawn tangent to the previous arc segment.
Specify length of chord:
Close
Closes a polyline with an arc segment.
Direction
Specifies a starting direction for the arc segment.
Specify the tangent direction from the start point of arc: Specify a point (2)
Specify endpoint of arc: Specify a point (3)
 Halfwidth
Halfwidth
Specifies the width from the center of a wide polyline segment to one of its edges.
Specify starting half-width
Specify ending half-width
The starting half-width becomes the default ending half-width. The ending half-width becomes the uniform half-width for all subsequent segments until you change the half-width again. The starting and ending points of wide line segments are at the center of the line.
Typically, the intersections of adjacent wide polyline segments are beveled. No beveling is performed for nontangent arc segments or very acute angles or when a dot-dash linetype is used.
Line
Exits the Arc option and returns to the initial PLINE command prompts.
Radius
Specifies the radius of the arc segment.
Specify radius of arc: Specify a distance
Specify endpoint of arc or [Angle]: Specify a point or enter a
Endpoint of Arc
Specifies the endpoint and draws the arc segment.
Angle
Specifies the included angle for the arc segment.
Specify included angle:
Specify direction of chord for arc
Second Pt
Specifies the second point and endpoint of a three-point arc.
Specify second point on arc: Specify a point (2)
Specify end point of arc: Specify a point (3)
Undo
Removes the most recent arc segment added to the polyline.
Width
Specifies the width of the next arc segment.
Specify starting width
Specify ending width
The starting width becomes the default ending width. The ending width becomes the uniform width for all subsequent segments until you change the width again. The starting and ending points of wide line segments are at the center of the line.
Typically, the intersections of adjacent wide polyline segments are beveled. No beveling is performed for nontangent arc segments, very acute angles, or when a dot-dash linetype is used.
Close
Draws a line segment from the current position to the starting point of the polyline, creating a closed polyline.
Halfwidth
Specifies the width from the center of a wide polyline line segment to one of its edges.
Specify starting half-width
Specify ending half-width
The starting half-width becomes the default ending half-width. The ending half-width becomes the uniform half-width for all subsequent segments until you change the half-width again. The starting and ending points of wide line segments are at the center of the line. Typically, the intersections of adjacent wide polyline segments are beveled. No beveling is performed for nontangent arc segments or very acute angles or when a dot-dash linetype is used.
Typically, the intersections of adjacent wide polyline segments are beveled. No beveling is performed for nontangent arc segments or very acute angles or when a dot-dash linetype is used.
Length
Draws a line segment of a specified length at the same angle as the previous segment. If the previous segment is an arc, the new line segment is drawn tangent to that arc segment.
Specify length of line: Specify a distance
Undo
Removes the most recent line segment added to the polyline.
Width
Specifies the width of the next line segment.
Specify starting width
Specify ending width
The starting width becomes the default ending width. The ending width becomes the uniform width for all subsequent segments until you change the width again. The starting and ending points of wide line segments are at the center of the line.







 With either method, you create an ordinary drawing file that can be inserted as a block into any other drawing file. Using WBLOCK is recommended when you need to create several versions of a symbol as separate drawing files, or when you want to create a drawing file without leaving the current drawing.
With either method, you create an ordinary drawing file that can be inserted as a block into any other drawing file. Using WBLOCK is recommended when you need to create several versions of a symbol as separate drawing files, or when you want to create a drawing file without leaving the current drawing.
 If you insert a block that uses different drawing units than the units specified for the drawing, the block is automatically scaled by a factor equivalent to the ratio between the two units.
If you insert a block that uses different drawing units than the units specified for the drawing, the block is automatically scaled by a factor equivalent to the ratio between the two units. Xrefs contained in a drawing you insert may not be displayed properly unless the xref was previously inserted or attached to the destination drawing.
Xrefs contained in a drawing you insert may not be displayed properly unless the xref was previously inserted or attached to the destination drawing. Insert Blocks at Intervals
Insert Blocks at Intervals To reduce the size of a drawing, you can purge unused block definitions.
To reduce the size of a drawing, you can purge unused block definitions. The block definition in the illustration comprises a name, PLUG_VALVE, four lines, and a base point at the intersection of the two diagonal lines.
The block definition in the illustration comprises a name, PLUG_VALVE, four lines, and a base point at the intersection of the two diagonal lines. You can also use the Block Editor to create blocks that are saved within a drawing.
You can also use the Block Editor to create blocks that are saved within a drawing.

 Draw Arcs by Specifying Start, Center, End When you know the start point, center point, and endpoint, you can draw an arc by specifying either the start point or the center point first. The center point is the center of a circle that the arc is part of.
Draw Arcs by Specifying Start, Center, End When you know the start point, center point, and endpoint, you can draw an arc by specifying either the start point or the center point first. The center point is the center of a circle that the arc is part of. Draw Arcs by Specifying Start, Center, Angle
Draw Arcs by Specifying Start, Center, Angle The included angle determines the endpoint of the arc. Use the Start, End, Angle method when you know both endpoints but cannot snap to a center point.
The included angle determines the endpoint of the arc. Use the Start, End, Angle method when you know both endpoints but cannot snap to a center point.
 The length of the chord of the arc determines the included angle.
The length of the chord of the arc determines the included angle.
 Conversely, after you complete a line, you can start an arc tangent to the line at an endpoint by starting the ARC command and pressing ENTER at the Specify Start Point prompt. You need to specify only the endpoint of the arc.
Conversely, after you complete a line, you can start an arc tangent to the line at an endpoint by starting the ARC command and pressing ENTER at the Specify Start Point prompt. You need to specify only the endpoint of the arc. You can create breaks in most geometric objects except
You can create breaks in most geometric objects except The portion of the object is erased between the two points that you specify. If the second point is not on the object, the nearest point on the object is selected; therefore, to break off one end of a line, arc, or polyline, specify the second point beyond the end to be removed.
The portion of the object is erased between the two points that you specify. If the second point is not on the object, the nearest point on the object is selected; therefore, to break off one end of a line, arc, or polyline, specify the second point beyond the end to be removed. In case you break any object wrongly or you deliberately want to combine two or more objects to form a single object you can JOIN them if the meet the criterion for this.
In case you break any object wrongly or you deliberately want to combine two or more objects to form a single object you can JOIN them if the meet the criterion for this.
 An object can be one of the cutting edges and one of the objects being trimmed. For example, in the illustrated light fixture, the circle is a cutting edge for the construction lines and is also being trimmed.
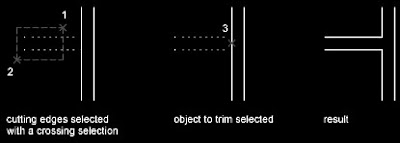
An object can be one of the cutting edges and one of the objects being trimmed. For example, in the illustrated light fixture, the circle is a cutting edge for the construction lines and is also being trimmed. 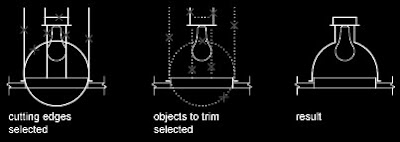 When you trim several objects, the different selection methods can help you choose the current cutting edges and objects to trim. In the following example, the cutting edges are selected using crossing selection.
When you trim several objects, the different selection methods can help you choose the current cutting edges and objects to trim. In the following example, the cutting edges are selected using crossing selection.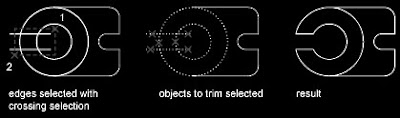 The following example uses the fence selection method to select a series of objects for trimming.
The following example uses the fence selection method to select a series of objects for trimming. You can trim objects to their nearest intersection with other objects. Instead of selecting cutting edges, you press ENTER. Then, when you select the objects to trim, the nearest displayed objects act as cutting edges. In this example, the walls are trimmed so that they intersect smoothly.
You can trim objects to their nearest intersection with other objects. Instead of selecting cutting edges, you press ENTER. Then, when you select the objects to trim, the nearest displayed objects act as cutting edges. In this example, the walls are trimmed so that they intersect smoothly.
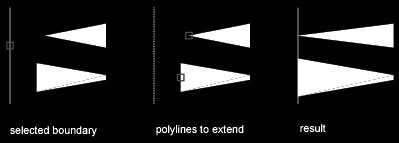
 You can extend objects without leaving the TRIM command. Hold down SHIFT and select the objects to be extended.
You can extend objects without leaving the TRIM command. Hold down SHIFT and select the objects to be extended.
 You can trim objects without leaving the EXTEND command. Hold down SHIFT and select the objects to be trimmed.
You can trim objects without leaving the EXTEND command. Hold down SHIFT and select the objects to be trimmed.
 For example, the following filter selects all circles except the ones with a radius greater than or equal to 1.0: Object =Circle
For example, the following filter selects all circles except the ones with a radius greater than or equal to 1.0: Object =Circle
 c. Window / Crossing – With this option a Window (from left to right) or a Crossing (from right to left) is drawn around the objects to be selected. The difference between Window and Crossing is – Window will select only the objects that are completely residing within its boundaries whereas crossing will select every object that intersects/falls within its boundaries. Therefore a crossing will always require smaller area to be covered as compared to a window as only the edges of the objects would be sufficient for selection.
c. Window / Crossing – With this option a Window (from left to right) or a Crossing (from right to left) is drawn around the objects to be selected. The difference between Window and Crossing is – Window will select only the objects that are completely residing within its boundaries whereas crossing will select every object that intersects/falls within its boundaries. Therefore a crossing will always require smaller area to be covered as compared to a window as only the edges of the objects would be sufficient for selection. 



 These FOUR are the commonly used and basic methods of object selection. These options also have sub options like –
These FOUR are the commonly used and basic methods of object selection. These options also have sub options like – 